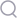
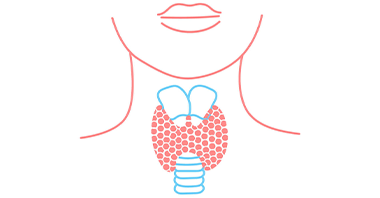
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland which is located at the base of the neck, below the Adam's apple. It comprises of the right lobe and left lobe which is connected by a thin piece of tissue called the isthmus. Importance of Thyroid gland: The thyroid gland is a part of the endocrine system which is made up of glands that produce, store and release hormones into the bloodstream. The hormones released by the thyroid gland is accountable for metabolism, growth and development in the human body. The Thyroid gland plays a vital role in the function of many systems and organs such as the heart, brain, liver, kidneys and skin. So, it is important to understand how the thyroid gland works and to be aware of warning signs of thyroid gland problems before its late. Thyroid cancer: Thyroid cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the thyroid gland when cells mutate or change. These abnormal cells begin multiplying uncontrollably in your thyroid and form a tumour. Thyroid cancer is seen more in women than in men. Women usually tend to get thyroid cancer at the age between 40-50s, while men get it in their 60s. The thyroid gland has two main types of cells: 1. Follicular cells: Follicular cells are also called as thyrocytes or thyroid epithelial cells, responsible for the secretion of iodine-containing thyroid hormones - thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). The amount of thyroid hormone discharged by the thyroid is controlled by the pituitary gland at the base of the brain, which makes a substance called thyroid-stimulating hormone. 2. C cells: C cells are also called parafollicular cells whose primary function is to secrete calcitonin, a hormone that helps to regulate how the body uses calcium. Causes: Thyroid cancer is associated with a number of inherited conditions, yet the definite reason for thyroid cancer is not yet found. Some of the risk factors that can’t be changed are gender and age, hereditary and family history. Some of the risk factors that may be changed are iodine levels in diet and radiation exposure. Types of Thyroid Cancer: 1. Papillary Thyroid Cancer: Papillary thyroid cancer is the most common type of thyroid cancer, found in up to 80% of thyroid cases. It tends to grow slowly and often spreads to cervical lymph nodes. It can occur at any age, but it often affects people aged between 30-50. 2. Follicular Thyroid Cancer: Follicular thyroid cancer is the second most common type of cancer that arises from follicular cells of the thyroid. It can occur in people aged more than 50 and tends to spread into your lymph nodes and most likely into blood vessels. This type of cancer is seen in countries where people don’t get sufficient iodine in their diet. 3. Medullary Thyroid Cancer: Medullary thyroid cancer develops in thyroid cells called C cells. These C cells produce a hormone called calcitonin which helps control the amount of calcium in the blood. This cancer is seen in about 4% of all thyroid cancer cases, and it can spread in lymph nodes, lungs or liver before a thyroid nodule is found. 4. Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer: Anaplastic thyroid cancer is a rare and severe type of cancer to treat, as it is aggressive in spreading to other parts of the body. It is also called as undifferentiated carcinoma, seen in 2% of all thyroid cancer cases. Symptoms: Normally, thyroid cancer does not have any signs or symptoms at an early stage. As it grows, it may cause: 1. Neck pain and throat pain 2. Swollen lymph nodes in the neck 3. Difficulty swallowing 4. Voice changes, hoarseness Many types of tumours can develop in the thyroid gland, that includes non-cancerous (benign) and cancerous (malignant), which tend to spread into nearby tissues and to other parts of the body. If you experience any of these signs then it's time to consult the doctor to know the root cause which may or may not be thyroid cancer. Diagnosis: First your doctor/physician will take a detailed medical history and conduct a careful physical assessment of the thyroid gland. The following are the tests included in the diagnostic process. 1. Fine needle aspiration biopsy is a simple procedure used to remove a sample of cells, or tissue for microscopic examination to determine cancer. 2. Ultrasonography is required as guidance of fine needle biopsy if the nodule or lump is difficult to evaluate. 3. Thyroid scan is an imaging procedure that uses radioactive iodine tracer to check the functioning of the thyroid gland especially for patients with low TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) levels to evaluate thyroid nodules that are usually benign. 4. Blood tests are done to determine if the thyroid gland is functioning normally. Thyroid Cancer Treatment: Based on the severity of thyroid cancer, you may need more than one type of treatment. 1. Surgery 2. Thyroid hormone therapy 3. Radioactive iodine 4. External radiation therapy 5. Chemotherapy 6. Injecting alcohol into cancers 7. Targeted drug therapy 8. Palliative care If you are looking for best cancer hospitals in Bangalore, then Sakra Premium Clinic is the top-recommended hospital that is offering multi-speciality facilities and advanced treatment services. We have a team of expert cancer specialists with the support of skilled staff to provide comprehensive cancer care. Book an appointment online with our top cancer specialists and get advice for the right treatment options for thyroid cancer.
Other common cells in the thyroid gland include lymphocytes which are part of the immune system and stromal cells which are supportive cells.