.jpg)
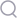
What are sinuses? Sinuses are air-filled cavities in our skulls. There are four pairs of sinuses.The maxillary,ethmoid,frontal & sphenoid.The purpose of sinuses is to moisturise the air we breathe, keep our head lighter(due to air in them-hence when they are filled with mucus we get heavy-headed) & they also enhance our voice. What causes Sinusitis in a Child? What are the symptoms of sinusitis in a child? If the nasal septum deviates too far or there are nasal polyps or obstruction of any kind, it will lead to blockage in the free flow of nasal mucus & eventually sinusitis. How do we diagnose sinusitis? Role of nasendoscopy in the OPD is to add to the information given by patient & is more useful for looking for polyps & other obstruction which cannot be easily picked up by anterior headlight examination. If your symptoms do not clearly indicate that you have sinusitis or if they persist for a long time and do not get better with treatment, we may order a CT (computerized tomography) scan to confirm that you have sinusitis. To look for causes of chronic sinusitis, we may order blood tests, take a sample of nasal mucopus or order sweat test. What is the management of sinusitis? Most of the acute sinusitis resolve with nasal decongestion, treatment of nasal allergy & symptomatic pain treatment. However, if the symptoms do not resolve with these methods then antibiotics are given. Do not use decongestant nasal spray without checking with the child’s doctor. Chronic rhinosinusitis is often a challenge to treat. Surgery is offered if medical management fails.
There are four different sinuses:
What is sinusitis in children?
Sinusitis is inflammation or infection of sinuses which could be allergic, viral or bacterial.
There are 3 types of sinusitis:
Sinuses get blocked with discharge and bacteria starts growing in them which leads to sinus infection or sinusitis. The most common bacteria that cause sinusitis are streptococcus pneumonia, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis.
The common symptoms are:
Diagnosis is usually done clinically by your symptoms & examination of the nose. In the nasal examination, we look for inflammation, mucopus & any obstruction or swellings. There can also be associated with facial tenderness over sinuses.
Medical treatment is offered first in the form of Nasal steroid sprays. A long course of antibiotics is occasionally recommended.
Saltwater or saline nasal sprays can be helpful in chronic rhinosinusitis because they remove thick secretions and allow the sinuses to drain.
Oral steroids may be prescribed for severe chronic rhinosinusitis especially if an allergy is suspected.
The doctor will recommend having fluids every hour. It helps thin mucus and allows it to drain more easily.
The goal of surgery is to improve sinus drainage and reduce blockage of the nasal passages. Nasal surgery usually is performed to accomplish the following:
Enlarge the natural openings of the sinuses
Remove nasal polyps
Correct structural problems inside the nose and the sinuses if they contribute to sinus obstruction
Although most people have fewer symptoms and a better quality of life after surgery, problems can reoccur, sometimes even after a short period of time in allergics.
In children, problems can sometimes be avoided by removing the adenoids. Adenoids are gland-like tissues, located high in the throat behind and above the roof of the mouth, can obstruct the nasal passages.
What are the complications of sinusitis?
Complications are rare. However, they can be serious. For example, the infection may spread from sinus to around an eye, into bones, into the blood, or into the brain.
These severe complications are estimated to occur in about 1 in 10,000 cases of acute sinusitis and are more common in children with infection of the frontal sinus.
Children are more prone to complications than adults. Swelling or redness of an eyelid or cheek in a child with sinusitis should be reported urgently.
How can sinusitis be prevented?
There are no scientifically proven methods to prevent acute or chronic sinusitis. However, the following ways can help: